On the 8th annual Energy Efficiency Day, Oct. 4, Yardi Energy will join thousands of organizations in the U.S. and Canada in sharing ideas for reducing energy waste and expanding energy efficiency. Energy Efficiency Day provides a forum for U.S. and Canadian corporations, local governments, universities, utilities and other organizations to document such initiatives as upgrading lighting, building insulation and heat pumps and establishing partnerships with local utility companies to reduce stress on the grid during peak demand. The day helps those occupying and investing in residential, commercial, affordable and other property types “share tips, tools and stories that promote the multiple benefits of energy efficiency, [which is] the cheapest, quickest way to meet our energy needs, cut consumer bills and reduce pollution,” says the Energy Efficiency Day organization, a coalition of U.S. energy efficiency advocacy groups. Energy Efficiency Day holds special resonance for Yardi because it involves “a core component of our mission as a real estate technology provider. It’s a great opportunity to focus attention on the critical issue of energy performance, spur action and inspire long-term thinking about what’s needed to create a positive energy future,” adds Joe Consolo, Yardi industry principal for energy. In March, Yardi received the 2023 ENERGY STAR® Partner of the Year Sustained Excellence Award after being named Partner of the Year for five consecutive years. The Yardi ESG software suite enables green energy procurement, whole-building energy water and waste data aggregation, and reduced energy usage in residential and commercial properties. The company has also maintained ENERGY STAR certification for its corporate headquarters in Goleta, Calif. Learn more about ways to maximize the impact of Energy Efficiency Day, including a toolkit for promoting your efforts on social media channels, joining the conversation and finding news about energy efficiency...
GRESB Holds Key
To ESG Improvement
The buildings sector accounts for about a quarter of Canada’s total final energy consumption and approximately 15% of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions when emissions are associated with electricity used in buildings, according to Efficiency Canada. Canada’s buildings, which require both heating and cooling, are particularly reliant on energy use, which in most cases produces carbon. The government has committed to cutting the country’s greenhouse gas emissions by 40-45% below 2005 levels by 2030 and is set to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. Attaining these goals will require all sectors, including property management, to gain a clear understanding of their energy performance. That makes ESG a megatrend “that will continue to have a transformative impact on the industry,” says Richard Joy, executive director of Urban Land Institute Toronto. Gaining a deeper understanding of energy performance and how to improve it in 2022 will require real estate professionals to perform more energy benchmarking and better tracking of their buildings and portfolios’ energy performance. Leveraging accurate energy consumption data helps property owners confidently compare their performance against their own standards and others in their sector. Accessing this information in real time drives informed decision-making about productive building improvements and investments. “Technology and data analytics can assist with analyzing opportunities of growth and making better-informed investments,” notes Frank Magliocco, national real estate leader for PwC Canada. GRESB drives ESG insight A key resource for detailed energy performance information is the Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark (GRESB), an organization that benchmarks real estate assets’ environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance and provides standardized and validated ESG data to the capital markets. GRESB evaluations help real estate stakeholders improve their sustainability performance and satisfy growing investor demand for timely, reliable and accurate ESG information. The 2021 global GRESB evaluation measured...
Cleaner Trucks Initiative...
NOx Regulations
A recent proposal to tighten nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions aims to improve air quality. As a side effect, the changes will undoubtedly impact businesses. Can businesses expect to see shipping prices increase as fleet overhead rises? NOx is a type of air pollution formed during the combustion process in motor vehicles. The particulates have an adverse reaction on the environment and human health. By 2025, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) calculates that more than 33 percent of NOx emissions will spew from heavy-duty trucks. To decrease those projected emissions, the EPA is drafting a new set of NOx emission regulations. The EPA recently initiated the Cleaner Trucks Initiative. The legislation updates federal NOx regulations, which have not been revised since 2001. Additionally, the proposal creates a single federal rule for an incongruent batch of federal and state guidelines. Several air agencies have petitioned the EPA for clearer guidelines and tighter standards for the trucking industry. The new plan will help to streamline compliance standards while promoting transport efficiency. The resulting changes will result in less particular matter and cleaner air. “The Cleaner Trucks Initiative will help modernize heavy-duty truck engines, improving their efficiency, and providing cleaner air for all Americans,” said Acting Administrator Andrew Wheeler said during a press conference. The initiative builds upon the success of previous legislation. Between 2007 and 2017, NOx emissions declined by 40 percent. The new challenge is to continue NOx emission decline without hindering economic growth. John Mies, manager of corporate communications for Volvo Group North, has been a vocal supporter of the proposal. Past legislation has been “challenging but practical” he said. He added, “This is a great opportunity to update and streamline the certification and compliance processes, ensuring a focus on real-world emissions control with minimal impediment...
Investing in Efficiency
Green multifamily financing
The importance of technology, including solutions provided by Yardi, in improving building energy performance is well documented. Perhaps less widely known, but no less crucial, is the role energy-oriented financial incentives play in helping property owners afford to invest in energy efficiency upgrades. Until recently, the Institute for Market Transformation (IMT) noted in a recent article, “building owners seeking more energy-efficient buildings had to seek out nontraditional financing and keep their energy upgrades separate from a traditional mortgage.” Today, a growing number of multifamily as well as commercial and affordable housing mortgages include sustainability incentives. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac have emerged as leaders in this new era of energy-efficiency financing. Under Freddie Mac’s Multifamily Green Advantage® suite of offerings, property owners who commit to reducing energy or water consumption by at least 25%, as verified by EPA’s ENERGY STAR® Portfolio Manager®, can receive better pricing and funding to make those improvements. Properties already green-certified may be eligible for rewards. “We’ve purchased nearly $18 billion in loans and helped finance 184,000 units in just the first 16 months of the program since launch in 2016. We’re proud to be making a real difference for borrowers, renters and the environment,” Freddie Mac said in a November 2017 statement. In May 2018, Richard Meyer, a Freddie Mac official presenting on a panel at a Yardi Executive Briefing, reported $21.7 billion in financing to date. Meanwhile, Fannie Mae’s green financing for multifamily properties has offered mortgage financing to cover energy and water efficiency improvements in apartment buildings and cooperatives since 2012. Through 2017, the program has contributed to the upgrading of 248,000 units with new equipment, saving enough electricity to power 80 million cell phones and enough water to fill 42 billion glasses. “These improvements improve the property’s bottom line with lower utility costs, improve the quality and affordability of housing for tenants, and increase the property’s environmental sustainability,” the Fannie Mae website says. Green financing comprises more than 40% of Fannie Mae’s multifamily loans – about $31 billion during 2017. Some smaller and nontraditional channels, such as community development financial institutions (CDFIs), offer alternative financing. One CDFI, New York City’s Community Preservation Corporation, underwrites multifamily property financing for energy efficiency improvements into its traditional first-mortgage loans. Whichever program is used, it’s clear that property owners benefit. IMT Executive Director Cliff Majersik, speaking at the May 2018 Yardi Executive Briefing, said that a soon-to-be-released study of 50 green-certified residential buildings shows that those properties averaged $6 higher revenue per square foot per year than non-certified buildings; after accounting for some increased expenses, the NOI per square foot increased by more than $4.50. More recently, the IMT reported on a six-floor, 34,600-square-foot multifamily walk-up for which New York’s Community Preservation Corporation provided $1.4 million in construction and mortgage financing for a roof-to-cellar renovation. New LED lighting, low-flow showerheads and faucets, refrigerators and other upgrades reduced the property’s annual utility cost by $23,000. Prior to the overhaul, the owner historically spent about $2,210 per apartment on annual utility expenses; the retrofit decreased the cost to $1,540 per apartment, an annual savings of about 30%. “Key [market] players . . . must be aware of critical building components that affect energy efficiency—and be willing to integrate these details into their loan proposals. Mortgage brokers have a unique ability to impact loan amounts when successfully factoring in energy efficiency [and] can help leverage all players in a buildings lifecycle and acknowledge that investing in energy efficiency is both good for business and good for the environment,” says the July 2018 IMT article, which is available in its entirety...
Benchmarking Bonus
NAA Return on Energy
Currently, over 45% of the US commercial building market uses the ENERGY STAR®, the US EPA’s voluntary certification program designed to measure energy efficiency and improve resource management. At the heart of ENERGY STAR® lies the ability to track energy usage data to reduce energy consumption and improve building performance. “It all starts with taking a look at what you have and seeing what [information] you’re tracking and what data is available,” Craig Haglund, Program Manager, for the US EPA’s ENERGY STAR program, said in the National Apartment Association’s recent webinar, Financial Success with Energy Benchmarking. With comprehensive data collection and analytics capabilities, US EPA’s Portfolio Manager works in concert with ENERGY STAR for complete resource management oversight. “They say ‘you can’t manage what you can’t measure,’ which is 100% true,” Haglund continued, “but that misses what you can do with all that data.” Whole Building Consumption For building owners and managers interested in tracking their energy, water and waste metrics, ENERGY STAR provides an easy, comprehensive management tool: Portfolio Manager. With Portfolio Manager, building data can be tracked and analyzed. Users can create customized reports and monitor changes in energy, water, greenhouse gas emissions and more. “Portfolio Manager literally includes hundreds of measurement metrics,” explained Haglund. “Standardized reports can help users assess portfolio performance and share that information or integrate it into other presentations.” Those measurement metrics can be applied to any sized property portfolio, from one building to, in the case of East Coast real estate services firm Bozzuto Management, 63,000 units spread out over 220 communities and representing 2.1 million square feet of mixed-use development. “We have been using Portfolio Manager since 2012,” said Bozzuto’s Director of Sustainability, Peter Zadoretzky. “Over the last couple of years, we’ve gone from a messy,...
Grid-Sized Storage
Energy Efficiency
Late last month, Southern California Edison switched on its newest substations, an 80MWh lithium-ion battery storage facility that will manage peak demand and improve grid reliability. Just off Interstate 15, nestled in the heart of California’s Riverside County, one of the world’s biggest energy storage projects recently roared to life. Part of a collaboration between Tesla and Southern California Edison (SCE), the installation at the Mira Loma substation will be used to manage peak energy demand and stabilize the grid. “Upon completion, this system will be the largest lithium-ion battery storage project in the world,” declares a Tesla blog post announcing the project. “When fully charged, this system will hold enough energy to power more than 2,500 households for a day or charge 1,000 Tesla vehicles.” Managing Peak Energy The Mira Loma project is one of the first to use Tesla’s new Powerpack 2 for utility-scale energy storage. With an 80 MWh capacity, the 400 Powerpacks will allow SCE to manage energy use during peak hours. The Powerpacks will be charged with electricity generated during off-peak hours and then supplement demand during periods of peak demand. This process will not only save energy; it will allow SCE to maintain grid reliability, deliver better power quality to customers and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. “The system will charge using electricity from the grid during off-peak hours and then deliver electricity during peak hours to help maintain the reliable operation of Southern California Edison’s electrical infrastructure which feeds more than 15 million residents,” explains the Tesla statement. “By doing so, the Tesla Powerpack system will reduce the need for electricity generated by natural gas and further the advancement of a resilient and modern grid.” Future Expansion Larger utility-scale energy storage projects are already in the works...
The Pulse of Energy
Yardi Energy
With the ability to collect, analyze and communicate real-time energy information, Pulse Energy adds the power of data to Yardi Energy arsenal. The Power of Data Over the last few years, Jeff Rambharack and the Pulse Energy team have worked to collect data on over a million businesses throughout the US and Canada. That data drives the company’s overall approach and helps provide Pulse clients with strategies tailored to their unique challenges. The company works with utilities and individual businesses, focusing on solutions specifically for different industry segments. “We provide personalized messaging for individual businesses,” explains Rambharack. “We support over 130 different verticals for businesses segments, and we provide personal messaging within each segment. We recognize that every business is different, and we work to identify sources of energy consumption and provide targeted recommendations layered on top of our in-depth analytics we’ve developed to analyze each business’s energy consumption.” Rambharack believes the biggest benefit of this data aggregation is that it allows an energy usage analysis at every level of a company’s organization. By being able to provide personalized insights about of those levels of aggregation, Pulse clients can pursue more effective energy management policies and procedures to reduce energy waste and improve energy efficiency. “Just being able to provide insights and say ‘Hey, you should go look at building X, because we think it has some efficiency problems,’ is so valuable to our clients,” says Rambharack. “Maybe we discover that they are leaving their systems on at night or running their AC and heating simultaneously. Our analytics and extensive database help us detect these sorts of oversights and provide valuable energy consumption insight to our customers.” Tracking Usage against the Baseline One of the most valuable tools for energy management involves developing an accurate...
Solar Surfaces
Energy Produced in Place
A revolutionary new technology can put solar cells on almost any surface, transforming traditional solar energy installations and turning buildings into power generators. Rising up from suburban sprawl like the mythical Oz, the downtown business district of any major metropolis repeats a familiar scene: high-rise office buildings, covered in windows, reaching for the sky. Skyscrapers may typify city skylines, but all that reflective glass also represents an incredible opportunity. Imagine harnessing all that surface area by converting those reflective surfaces into powerful solar arrays. That’s the idea behind Santa Barbara-based startup Next Energy Technologies groundbreaking solar technology. Surface Generation Currently, buildings account for anywhere between 40-50% of total global energy use and over half of all CO2 emissions. In addition, electricity represents one of the largest variable operating expenses building owners face, accounting for as much as 20-25% operational budgets. Many facilities successfully reduce consumption by incorporating renewable energy onsite and energy efficiency strategies like LED lighting and energy management systems. But what if the buildings themselves could generate power? The concept is deceptively simple: use transparent solar cell ink to print photovoltaic cells directly between standard dual-pane windows. The genius lies in the execution. For Next Energy founders Daniel Emmett and Corey Hoven, it’s all about making solar efficient, customizable and inexpensive. Windows Transformed “The most important difference with our technology is the transparency,” Hoven explains. “While all other solar cells are opaque and absorb all visible light, the windows that use our system look like conventional windows. They can allow the visible spectrum to get through, which makes our solar cells highly efficient without changing the appearance or functionality of the window.” Tinted windows can help manage indoor temperatures and lessen heating and cooling costs, but adding a solar component ups the...
Sun vs. Snow
Rocky Mountain Institute
Touted as the one of the nation’s most energy efficient structures, the Rocky Mountain Institute’s new headquarters doesn’t just survive Colorado’s harsh winters – it thrives. With nighttime temperatures hovering around 5 degrees Fahrenheit in the winter, and an average of 90 inches of snow per year, Basalt, Colorado may not seem like the ideal spot for one of the world’s most energy efficient buildings. That didn’t stop the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) from choosing a new location along the Basalt’s Roaring Fork River for their new headquarters. With neighbors like Aspen and Snowmass, RMI’s property shines like a beacon amidst snowcapped mountains and knee-high drifts, but it’s the 252 days of sunlight per year that help this architectural set piece maintain 60-degree indoor temperatures even during the coldest night of the year. The surrounding ski resorts actually helped inspire the building’s structure. As Justin Brooks, lead designer ZFG Architects explains in an interview with Gizmodo, “It’s a very Colorado Solution. If you’re wearing a down jacket that’s highly insulated on the back, you can still sit outside and enjoy a beer.” RMI’s building follows similar logic. The building capitalizes on all those sunny days by using airflow, directed ventilation and solar panels to capture the solar gain from the south side of the building – which gets the most direct exposure to sunlight – and use it to manage the temperature inside. Rooftop solar panels and high-performance quad-pane windows also do their part, the former contributing to the structure’s power load and the latter trapping thermal energy. The building’s exterior also contributes, with a “super tight” building envelope and sunshades on the façade that move based on weather sensor data. Kinetic and responsive, the outside of the building excels at controlling glare and...
Dorm Rooms Get Green
Sustainable Collegiate Living
As demand for modern, energy-efficient and environmentally friendly campus housing continues to grow, colleges and universities are embracing a new era of sustainable student residences. Recent estimates by the DOE, EPA Energy Star, and ACEE reveal student housing represents a huge opportunity for energy efficiency in multifamily housing. With the chance to reduce energy use by up to 30% at new or existing properties, any energy efficiency or sustainability effort is sure to quickly meet (and probably surpass) initial ROI estimates. Currently, multifamily properties accumulate more than $30billion in energy costs annually – sometimes paid by tenants, but other times falling into the lap of owners and property managers. With an estimated $3.4 billion in energy savings possible, it makes sense for the student housing industry to focus on sustainability. Additionally, sustainable student housing presents an enormous marketing opportunity for property owners and managers: a recent poll revealed 60% of college students believe protecting the environment should be prioritized, and a whopping 76% support policies encouraging energy efficiency (rather than seeking new energy sources) to meet energy demands. Stylish and Sustainable in Seattle Initially conceived as a traditional, multi-story dorm designed to house 130 students, Bastyr University’s 2010 student housing project eventually transformed into a sustainable, LEED certified student village. Located just east of downtown Seattle, Bastyr University prides itself on its position at “the forefront of developing the model for 21st-century medicine.” With a multidisciplinary curriculum focused natural medicine, Bastyr University readily assumed the mantel of sustainable student housing pioneer. Bastyr’s Student Village is comprised of an 11-cottage complex spread out over 12 acres on Bastyr’s 52-acre campus. Each three-story cottage can house up to 12 students who have access to common areas, a central courtyard and a variety of sustainable features...
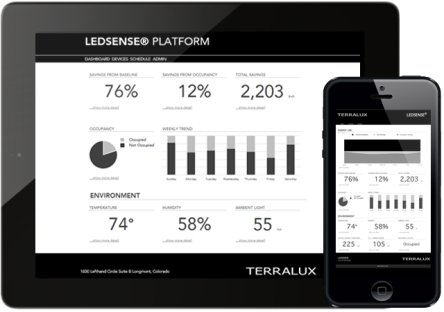
Ledsense
Smarter source of light
The Smart Home is a very entertained interest in the technology industry; nowadays it comes equipped with devices capable to increase comfort, protect occupants, and save on utility bills. Houses already have Nest – the smart thermostat, Goji – the smart lock, Tado Cooling – the air conditioning/ thermostat smart device, and Luna – the smart mattress cover. Using the smartphone as the device to turn on lights, lock doors, check humidity levels, and monitor energy use inside the home, requires a large data set, and systems must be programmed individually and connected to the controlling transmitter. Terralux, a LED lighting company, recently launched a new product named Ledsense, which is a cloud based lighting system with brain power. Looking at the evolution of LEDs, not too long ago, they were not only ineffective, but also very expensive; those were the shining times of the Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs). Since then things evolved and nowadays LEDs show increased improvement in efficacy, today demonstrating some of the highest light outputs – measured in lumens per watt – and at the same time, the economics of LEDs are compatible with other light sources. Slowly, but surely, LEDs are replacing CFLs, with more and more organizations looking to save money and deliver a lighting alternative that is friendly with the environment. The Ledsense platform integrates the LED light unit with sensor communication and control technology; it acts like an Internet of Things on LED lights. These units are quite amazing: they include sensors that can determine building temperature, sense motion from a person in the vicinity, and even sense odors and potentially toxic chemicals in the air. All this data is collected and then communicated back to the building owner, through the cloud. “A light is no...
Learning to Like LEDs...
Bulbs gain multifamily traction
Multifamily professionals are torn when it comes to LEDs. While many love the idea of a bulb that lowers utility bills without sacrificing brightness, they aren’t in love with the high upfront costs. It can also be hard to tell when it’s worthwhile to invest in LEDs when halogen, fluorescent, CFL, or even incandescent bulbs might suffice. A few tips might make the decision easier. When it comes to longevity, LEDs are hard to beat. LED lamps can last up to 50,000 hours, outliving the average incandescent bulb by more than 10 times. This makes them ideal for hard to reach places like stairwells, parking lot posts, and ceiling-mounted security fixtures. LEDs are also incredibly useful for fixtures that must stay lit day and night. The light emitting diodes also have less practical and more fashionable applications. LEDs are now more versatile than ever, making them ideal for eye-catching applications in hip, newly constructed buildings. Different colors and warmths allow lighting designers to explore endless interior and exterior possibilities. Like their incandescent cousins, LEDs can now be dimmed, a feature that designers have craved for years. There is even a new line of OLEDs with thin, flexible lamps that promise innovative new creations like poster-thin televisions for fitness centers and bedroom windows that turn into lamps at night. Though the advantages of LEDS are evident, you must first make sure that you can provide the proper housing for the bulbs to reap their full potential. The longevity of LEDs helps the lamps to pay for themselves in just 4-6 years but such returns aren’t a sure thing. James Youngston, IALD, LC Principal at Gabler-Youngston explains, “Retrofit lamps are rated for 50,000 hours but that’s based on turning them on is sockets by themselves, not...
Energy Efficiency Summit...
Yardi Sponsors UCSB event
Yardi is proud to be a silver sponsor of the 2013 UC Santa Barbara Summit on Energy Efficiency, where U.S. Secretary of Energy Steven Chu will be among the featured speakers. The event will take place May 1-2 at Fess Parker’s Doubletree Resort on the Santa Barbara Waterfront. The emphasis of this year’s summit, the fourth annual event, is “Materials for a Sustainable Energy Future.” Session foci will include: Materials for Energy Technologies: What are the key issues around extracting, processing and using the materials needed for our increasing global energy demands? Innovations in Solid-State Lighting: The latest developments in this growing field. Energy Efficient Information and Communications Technologies: The future of scalability and energy efficiency for next generation ICT core networks. Electrochemical Energy Storage Technologies: What are the latest technologies and materials that will enable more efficient, economical and reliable energy storage? Utilities Discussion: The need for, and implementation of, new technologies for energy efficiency. High Efficiency Power Electronics: Using materials to minimize energy loss and make power electronics more efficient on all levels. Keynote speakers scheduled to appear at the summit include: Dr. Steven Chu, Secretary of Energy, U.S. Department of Energy. Co-winner of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1997, Dr. Chu is a former Director of the Lawrence Berkeley National Lab and a distinguished professor of physics, molecular, and cellular biology. Michael McQuade, CTO and Senior VP for Science & Technology, United Technologies Corporation, who provides strategic oversight and guidance for research, engineering and development activities at UTC. George Crabtree, Director, Joint Center for Energy Storage Research (JCESR), Argonne National Laboratory. Also a Senior Scientist and Distinguished Fellow at Argonne, he has won numerous awards for his research, including the Kammerlingh Onnes Prize for his work on the physics of...